
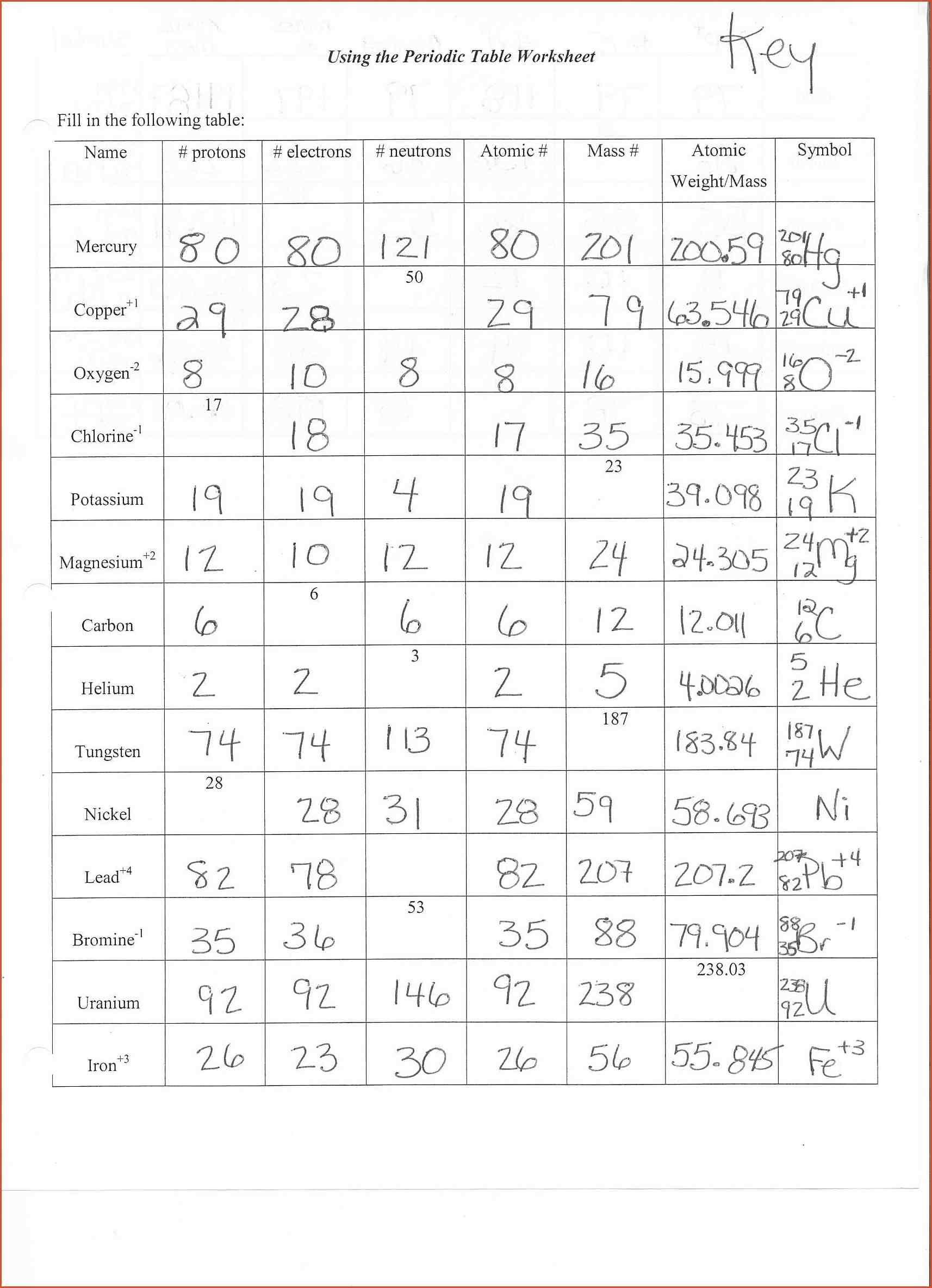

For example, the symbol for carbon is C, and the symbol for calcium is Ca. Each element has its own name and a one- or two-letter symbol (usually derived from the element’s English or Latin name). Neutrons in the nucleus have little effect on chemical behavior, and the protons are significant only because they determine how many electrons surround the nucleus in a neutral atom.Īll atoms with the same atomic number behave in much the same way chemically, and are classified as the same chemical element. These outer electrons are therefore the most important factors in the chemical behavior of atoms. When two atoms are close enough to combine chemically -to form chemical bonds with one another-each atom primarily “sees” the outermost electrons of the other atom. The mass number of an atom is equal to the total number of heavy particles: protons and neutrons. It is equal to the number of electrons around the nucleus, because an atom is electrically neutral.

The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is known as the atomic number, Z. The heaviest stable atom is lead-208, with a mass of 207.976 6521 Da. With this scale, protons and neutrons have masses that are close to, but not precisely, 1 u each (there are 6.022 x 10 23 u in 1 gram This number is known as Avogadro’s number, N, and one of the ways this number can be calculated is discussed below). A given atom has an atomic mass approximately equal (within 1) to its mass number times the atomic mass unit (for example the mass of a nitrogen-14 is roughly 14 Da), but this number will not be exactly an integer except (by definition) in the case of carbon-12. The atomic mass unit (amu) is defined as exactly one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom that has six protons and six neutrons in its nucleus. \): Charge and mass of three sub atomic particles Particle


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
